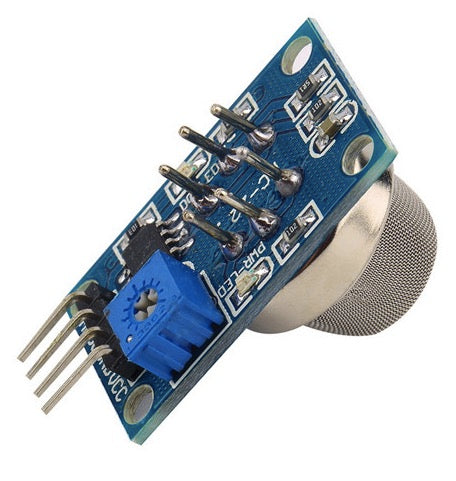
Description
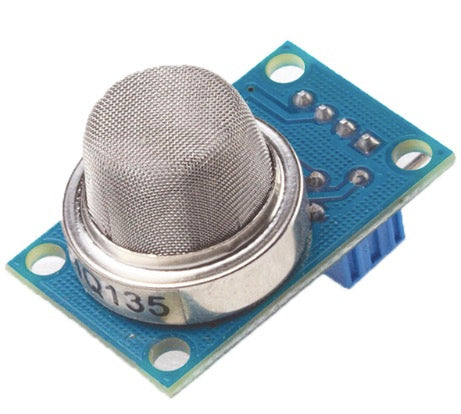
MQ135 Semiconductor Sensor is an air quality gas sensor having high sensitivity to ammonia gas, sulfide, benzene series steam, smoke and other toxic gases as well.
The SnO2 semiconductor material is used in the MQ135 for detecting the gases. It has a lower conductivity in clean air. It helps in detecting the rising levels of gases through rise in its conductivity. Users can convert the change of conductivity to gas concentration through a simple electronic circuit.
An MQ135 Air quality gas sensor has a wide array of applications such as:
- Air quality control equipment for buildings/offices
- Domestic gas alarm
- Industrial gas alarm
- Portable gas detector
The applicability of an MQ135 Air quality gas sensor is enhanced by the following features:
- Wide detecting scope
- Simple drive circuit
- Fast response
- High Stability
- High sensitivity
- Long-life
- Low cost
MQ135 Air Quality Sensor Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 2.5-5V
- Operating Current: 150mA
- Heat-up time: 20s
MQ135 Air Quality Sensor pin diagram
Pin1: It is VCC Pin. It is used to connect 2.5-5V to the sensor.
Pin2: It is GND Pin. It is used to connect GND to the sensor.
Pin3: It is digital output Pin. From this pin you will get digital data HIGH/LOW.
Pin4: It is analog output Pin. From this pin you will get analog data.
Circuit diagram of MQ135 Air Quality Sensor with Arduino
Pin connection of MQ135 Air Quality Sensor with Arduino
Connect the VCC pin of the sensor to the 5V pin of the Arduino UNO board.
Connect the GND pin of the sensor to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO board.
Connect the AO pin of the sensor to the A4 pin of the Arduino UNO board.
Arduino code for interfacing MQ135 Air Quality Sensor with Arduino
int sensorPin=A4;
int sensorData;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(sensorPin,INPUT);
}
void loop()
{
sensorData = analogRead(sensorPin);
Serial.print("Air Quality:");
Serial.print(sensorData, DEC);
Serial.println(" PPM");
delay(100);
}Arduino code working
Create a variable named sensorPin to the pin number of the Arduino UNO board where you have connected the AO pin of the sensor. In our case, it is A4 pin of the Arduino UNO board.
Create another variable named sensorData. We will use this variable to store the data that will be received by the Arduino from the sensor.
Inside the void setup block, set the baud rate for the serial communication and initiate the serial communication using Serial.begin() command.
Then use the pinMode() function to set the sensorPin as INPUT. The Arduino will use this pin to get the analog data from the sensor.
Inside the void loop() function, use sensorData variable to store the data that is received by the Arduino from the sensor.
Then, print the data on the serial monitor using the print and println command. In the line”Serial.print(sensorData, DEC); “, we are converting the sensor data into decimal.


